GUM DISEASE TREATMENT (PERIODONTAL TREATMENT)
Harmful bacteria in your mouth can cause gum disease, making your gums bleed, swell, and irritated. Gum disease or Periodontal Disease affects most adults or even younger ones.
During the early phase, we can treat them with regular dental cleanings and with practical oral care like brushing and flossing. But left untreated, this gum problem can worsen, leading to more serious oral health problems.
If ignored, gum disease can lead to loose teeth and diminished alveolar (jaw) bone, which is harder to treat. It’s therefore essential to know the signs of gum disease, so you can get treatment without delay if they happen. As with most dental ailments, we can easily prevent gum disease. However, management can be burdensome if they reach the worst state.
Healthy Gum and Diseased Gum
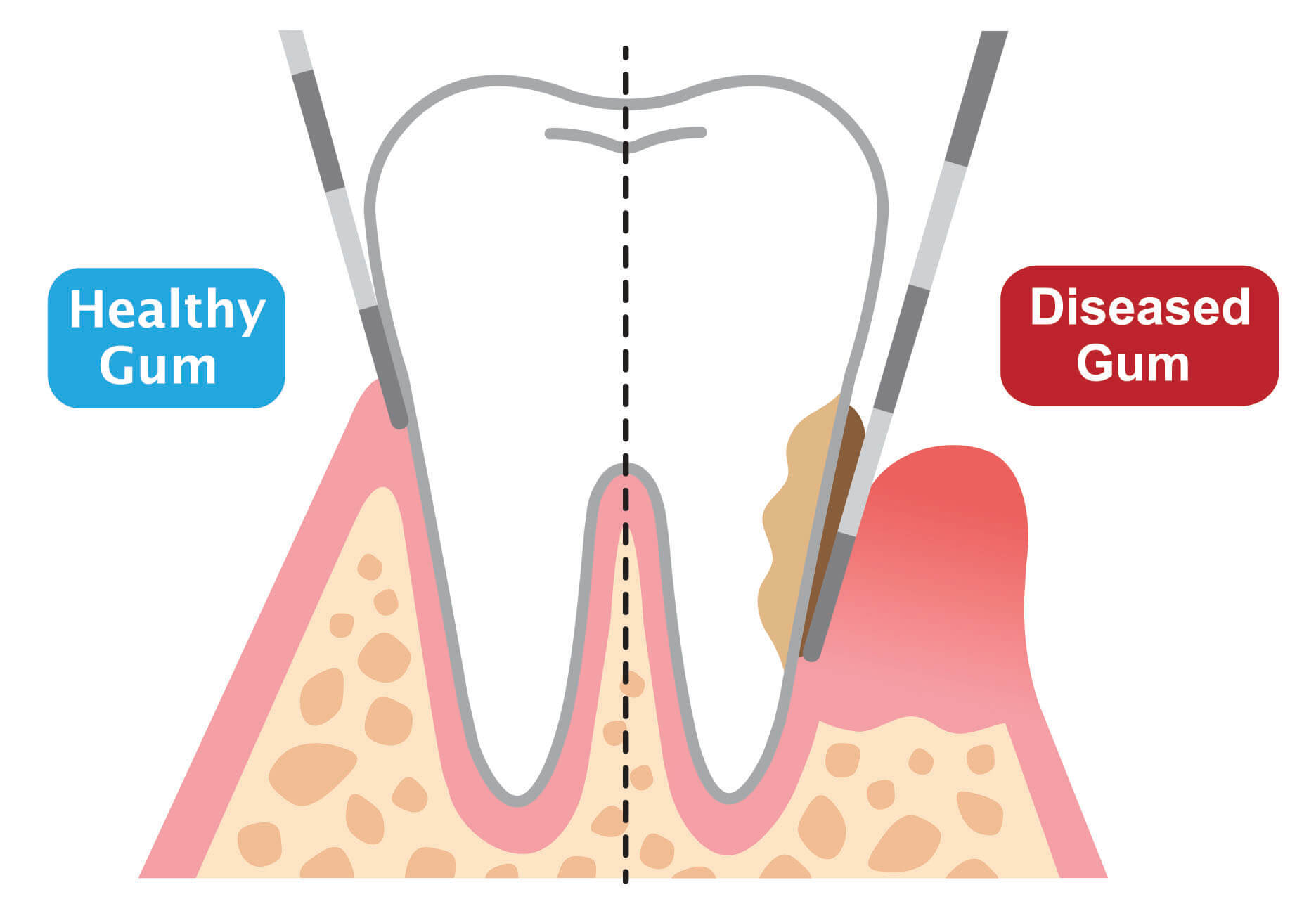
TWO STAGES OF GUM DISEASE
Gum disease can be recognized through two stages.
“Gingivitis,” which is an early-stage gum disease, is when the gums or gingiva become inflamed.
“Periodontitis,” the advanced stage, destroys the deeper connective tissues that support the teeth — including the alveolar (jaw) bone and the periodontal ligaments.
The Stages of Gum Disease
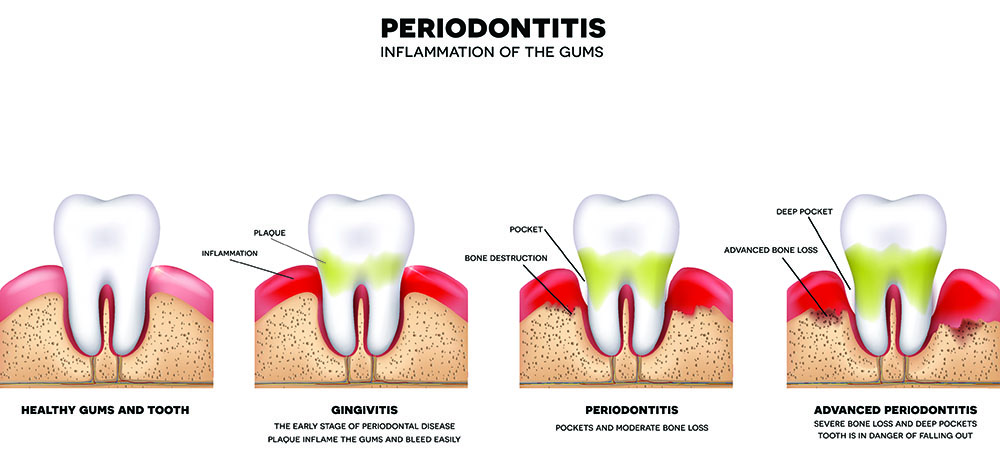
Gum disease may not be noticeable in the beginning, but the symptoms will become more evident as the disease progresses. Bleeding gums and pus are pretty clear signs.
Common symptoms include receding and inflamed gums, persistent bad breath, toothache, and pain in the teeth when biting or chewing.
Below are the warning signs for Gingivitis and Periodontitis:
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Early stages of gum disease include redness, tenderness, and swelling of the gums. You may also see traces of blood when you floss or brush your teeth. Eating hard or crunchy foods may be uncomfortable if they come in contact with your sore gums. People with gingivitis often have bad breath, even after brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
As gum disease gets worse, gaps (gum pockets) form between gums and teeth. The teeth may start to feel detached from their sockets or loose. Gum bleeding that’s occasional at first becomes more and more frequent. You might taste blood even when you’re not brushing or touching your gums. Also, the teeth may look longer than before, because the gums shrink back and the roots of the teeth become exposed. You’ll also be sensitive to cold, heat, and pressure because the tooth root is exposed.
Do you have any symptoms of gum disease?
Call our clinic to save your teeth and gums! Call us at :
You can schedule an appointment with us. Just give us a call beforehand so our dentist or periodontist can help you out.
Bacteria and Gum Disease Connection
There are way more bacteria in the mouth than in other parts of the body. Small crevices in the gums, cheeks, tongue and other mouth areas trap bacteria and gum disease-causing germs. Too much of bad bacteria can cause gum disease.
Easy Ways to Prevent Gum Disease
There are easy ways to stop gum disease. Regular and correct brushing and flossing can rid your teeth and gums of these bacteria. But if you don’t brush and floss regularly, the bacteria will grow and cause gum disease. These bacteria cause periodontal disease when they stay in your teeth and gums, which happens when plaque and dental calculus (tartar) harden.
Who is at risk of gum disease?
Having any of these increases your likelihood of getting gum disease:
– Cigarette Smoking
– Have diabetes, arthritis, heart disease, or disorders of the immune system like HIV and AIDS
– Do not brush your teeth properly or floss regularly
– Have crooked teeth, loose fillings, or poor-fitting dental appliances like bridges
– Have a close family member who has had gum disease or lost teeth early
Gum Disease: The Frequently Ignored Disease in the Mouth
Gum disease is an often ignored illness due to a lack of understanding of its effects. People with this disease usually don’t realize they have it until it gets bad and becomes hard to manage. Gum disorders can happen to anyone, regardless of their sex or age. Some people are more likely to get gum disease because of certain factors. Here’s why they happen:
1.) Cigarette Smoking –> causes dry mouth, which allows bacteria to flourish.
2.) Medications (such as steroids, pain relievers, and antidepressants) –> lead to
reduced saliva production, promoting bacterial growth.
3.) Advancing Age –> dry mouth becomes more common with age. As we mature,
the Mouth becomes more acidic, we produce less saliva, and we are more likely
to neglect oral hygiene.
4.) Hormonal Fluctuations –> as is evident in pregnant women and during post-
menopausal stage.
5.) Diabetes –> because the body’s decreased resistance to infections can
lead to gum disease becoming prevalent.
The Connection Between Gum Disease and Heart Disease
When you observe signs of gum disease, it is crucial to get dental help right away. If you don’t treat gum disease, you could lose your teeth. Studies show linking gum disease and heart disease. The bacteria that cause gum disease can damage the heart and blood vessels if they get into the bloodstream.
Gum Disease As Linked to Heart Disease
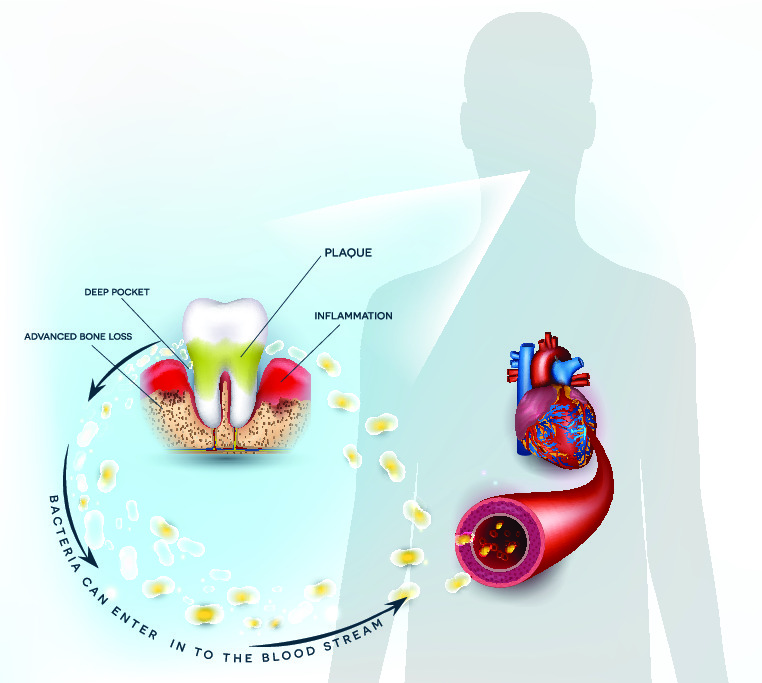
Gum Disease and Linked Illnesses – The Health Implications:
In their early stages, gum infections can lead to discomforting symptoms.
If not remedied, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss, making it difficult to eat. Moreover, the bacteria from the diseased gums can increase your likelihood of developing other health issues, such as:
Diabetes.
Heart disease.
Lung disease.
Stroke.
Arthritis.
TREATMENT OF GUM DISEASE
Non-Surgical Treatment
If your dentist detects the gum disease early, there is a big chance of reversing it. This can be done by improving home care for your teeth, gums, and eating habits.
Brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush is vital to avoid irritating delicate gums. Always brush your teeth thoroughly, including the gum line.
Brush teeth carefully, but not hurriedly. Use dental floss to remove food traps from between teeth – you can use ordinary floss or a floss threader.
The goal is to maintain clean teeth and not leave food debris or particles that harmful bacteria can feed on in your mouth.
A “water pik” or “water flosser,” a tool that bursts water on your teeth and effectively removes plaque and bacteria, is suggested for use.
You will also benefit from gargling an antiseptic mouthwash recommended by the dentist to eliminate persistent gum disease-causing bacteria.
If gingivitis symptoms do not go away with proper home care, we can use an antibiotic cream or gel to target the microorganisms. These microbes harm your gum health by infecting them and causing frequent bleeding and bad breath. Oral Prophylaxis (getting your teeth cleaned professionally) will help remove the “tartar” or hardened plaque. These deposits grow along the gum line, which contains bacteria that cause gingivitis.
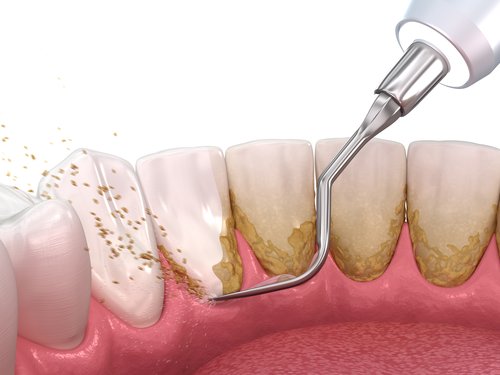
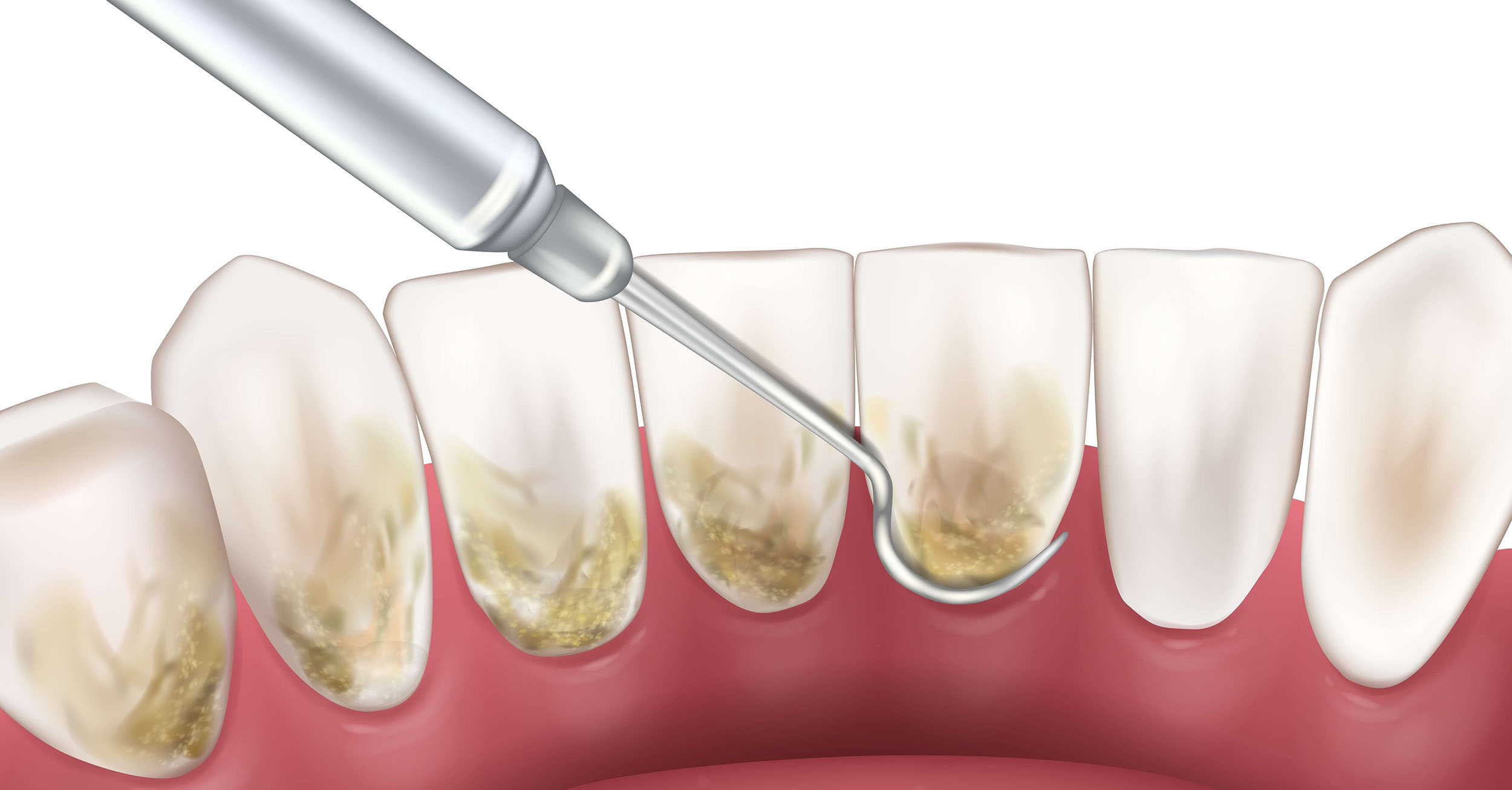
Deep Cleaning (Scaling & Root Planing)
Intensive teeth cleaning that involves the tooth crown surfaces and the part of the tooth root near the gum line may be necessary if a large amount of dental deposits (tartar) need to be removed.
Scaling and Root Planing, commonly called Deep Cleaning, is a more thorough cleaning procedure that requires local anesthesia or anesthetizing of the area to be treated for more convenience and minor discomfort.
The dentist will get dental x-rays to determine the severity of the periodontal problem. A periodontal probe will measure the “gum pockets” (spaces that form between the gums and teeth due to gum disease).
The dentist uses Ultrasonic Scalers (dental cleaning devices), which will be used to break down hardened plaque (“tartar”) and calculus deposits on the tooth surfaces.
The dentist may additionally use hand scalers and dental curettes. These specialized dental tools will remove stubborn calcular deposits clinging to the teeth surfaces, in between and around the tooth roots. He will thoroughly scrape off the dental plaque and tartar adhering on the tooth surfaces and below the gum line.
The purpose of Deep Cleaning (Scaling & Root Planing) is to clean and smoothen the teeth surfaces so that the gums can eventually attach to the teeth. Once the gums have healed, they will adhere to the teeth surfaces, preventing plaque and bacteria from accumulating.
Following this treatment, you may feel that treated gum areas will be sore for a few days. Be careful when brushing and cleaning, as you do not want to sever the newly treated gums. Brush your teeth carefully, and be cautious about eating foods not to harm the gums for continued healing.
Surgical Procedures for the Treatment of Extensive Gum Disease
Gum disease is a common condition that can cause various problems if treated incorrectly. Surgery might be necessary to treat gum disease in some cases. There are a few types of surgical procedures that can be used to treat gum disease, and your dentist will determine which treatment is right for you, depending on the severity of your condition.
Suppose you have pockets in your gums, loose teeth, receding gums, or other signs of Periodontitis. In that case, the dentist will manage your gum disease more extensively, or the periodontist will make the surgical approaches needed.
Flap Surgery is when the extra gum tissue is trimmed off, and the gum edges are correctly stitched. The purpose is to restrict plaque and bacteria from entering open gingival crevices, not to cause gum infection. Together with good oral care, antibiotic treatment comes along.
Tissue Grafts: The plaque and tartar that contains bacteria erodes the gums, periodontal ligaments, and even the alveolar jaw bone. The periodontist uses tissue grafts to see if your affected teeth can still stay in your jaw. If we go with this treatment, we’ll harvest tissue from the roof of the mouth and other donor areas and graft it onto the affected site.
Guided Bone Tissue Regeneration: One complication that can happen when your body’s trying to heal from gum disease is the gum tissue moving into the area where the bone tissue is. The periodontist may administer guided bone tissue regeneration to prevent this from occurring. A mesh is positioned along the edge of your gum tissue, holding it in place and stopping it from expanding into the bone space.
Gum Disease Treatment Cost
The cost of treating gum disease varies widely, depending on your dentist’s exact treatment. If you catch gum disease early, all you’ll need is a new toothbrush, some floss, and mouthwash.
Catching gum disease early is key to avoiding extensive and costly treatment later, and it’ll help you keep your teeth longer.
It is crucial to catch your gum disease early to avoid extensive and costly treatment down the line and keep your teeth for a long time.
Whether you are looking for a local dentist or the best dental clinic to help you with your routine dental cleaning, deep scaling, gum surgery or periodontal disease treatment, you will definitely find time for the necessary care. You must keep up with the necessary appointments and at-home care to treat your gum disease. Your teeth allow you to eat, and losing even one of them will greatly impact your ability to chew.
